 Standard scientific opinion has blamed weight gain on an excess of calories which is due to burning fewer than taken in. In opposition to this viewpoint, the carbohydrate-insulin model shows that the quality of diet matters more than calorie intake for weight loss. The model’s position is that eating processed carbohydrates and starchy foods leads to changes in hormone and insulin levels which results in an increase in fat deposition.
Standard scientific opinion has blamed weight gain on an excess of calories which is due to burning fewer than taken in. In opposition to this viewpoint, the carbohydrate-insulin model shows that the quality of diet matters more than calorie intake for weight loss. The model’s position is that eating processed carbohydrates and starchy foods leads to changes in hormone and insulin levels which results in an increase in fat deposition.
The increase in fat storage leads to hunger and the consumption of more foods rich in calories which then leads to obesity. This model has suggested that staying away from starchy and sugar rich foods might be necessary for losing weight instead of calorie restriction.
The WHO says that the worldwide prevalence of obesity and overweight has increased during the past 10 decades. There is an important consensus in the scientific community that the easy availability of these detrimental foods and also a sedentary lifestyles have contributed to the increase in obesity rates. However, there is a lot of disagreement as to how these environmental factors contribute to the problem.
According to the predominant EBM (energy balance model) eating more calories than those that are burned will result in weight gain due to a positive energy balance. The EBM has suggested that successful weight loss will require the reduction of total calorie consumption which means fewer calories and an increase in physical activity.
The CIM (carbohydrate insulin model) postulates that the quality of food eaten plays an important and critical role in management of body weight rather than the total caloric intake.
The EMB regards all calories in the exact way regardless of the their source. The problem is that the consumption of starchy and processed carbohydrates causes an increase in blood glucose which results in fat storage. As a result increased fat accumulation starts a feedback loop which results in increased hunger and the consumption of more foods rich in calories.
According to CIM it is the increased fat storage due to the consumption of processed carbohydrates and not the increased consumption of calories that actually leads to weight gain and is mostly responsible for elevated rates of obesity. Hormonal and metabolic changes which will occur due to eating specific foods are the main cause of weight gain with the excess calories being the outcome.
Reducing caloric intake tends to cause weight loss only in the short term. The is because the body adapts to the lower intake of calories which results in increased hunger and a lower metabolic rate.
The CIM postulates that food quality plays a more important role in the weight gain than the overall intake of calories. The intake of of carbohydrates has increased since the 1980’s and is likely because of the perception that eating fat causes weight gain.
The GI (glycemic index) rates carbohydrates due to how rapidly they increase blood glucose levels after consumption. The glycemic load is also a measure that can provide more comprehensive information about the surge in blood sugar levels.
The consumption of starchy and highly processed foods that have rapidly digestible carbs result in a blood glucose level surge. Foods with a high glycemic load such as potato products, refined grains and other foods high in starch are turned rapidly into free sugars.
As a contrast, proteins and fats have a minor impact on blood sugar level. Minimally processed grains, nuts, legumes, whole fruits and non-starchy vegetables typically have a moderate or low glycemic load.
A rapid surge of the glucose level after eating high glycemic foods will result in insulin secretion which regulates blood sugar and helps the liver, muscles, and fat tissue absorb glucose. At the same time, eating carbs that are rapidly digestible suppresses the level of glucagon, a hormone. The pancreas will secrete glucagon to counteract low blood sugar which occur between meals. The secretion of glucagon which is stored in the liver raises blood glucose levels.
In the course of the first 3 hours following the consumption of high glycemic foods, low glucagon and high insulin lead to glucose and fat storage. As a result, the body absorbs nutrients that are present in high glycemic foods in the first 3 to 4 hours and the low glucagon and insulin levels persist.
The hormonal state then slows down the breakdown of energy stored in the liver and adipose tissue which is required to fuel other critical body tissues. That causes low levels of fatty acids, glucose, and a variety of metabolites in the blood which resembles a fast-like state.
This drop in blood metabolites signal the brain that tissues are being deprived of energy. When the brain distinguishes the fast-like state, it evokes hormonal changes that lead to craving and hunger for foods that are high energy such as the foods that are high on the GI.
In animals it has been shown that all calories are not alike and that weight gain and obesity can also develop without an increase food intake. There is not yet proof of this in humans.
The CIM theory of weight gain has created a sizable amount of controversy which includes how carbs and insulin affect weight gain. There is a lot of individual variability in the changes and physiology that occur in individuals as they develop obesity. There could be some role for insulin, but there could be a lot of other factors. This makes it more challenging to identify the causes and then the potential treatments to help to prevent weight gain and obesity.
The implications of counting calories then subtracting those that may have been burned with physical activity, has challenges in terms of accuracy. This can be easily gamed so that a person thinks they are doing the right thing, but in fact they are not really accurately assessing the two components which can lead to poor results.
It is suggested that adhering to a diet that consists of low GI foods can lead to weight loss through increasing energy levels and reducing hunger. An important strategy is to replace high glycemic foods with high fat foods and allowing for a moderate consumption of whole fruits, legumes, nuts, whole grains and non-starchy vegetables.
To view the original scientific study click below:
The carbohydrate-insulin model: a physiological perspective on the obesity pandemic
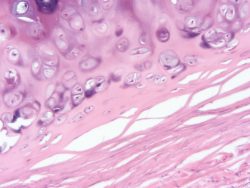 Research from the Univ. of Southampton has invented a novel way to use stem cells to generate tissue from human cartilage. This new technique could open up pathways for developing a much needed treatment for cartilage damage in people.
Research from the Univ. of Southampton has invented a novel way to use stem cells to generate tissue from human cartilage. This new technique could open up pathways for developing a much needed treatment for cartilage damage in people.


 There are certain locations in the US that seem to have a significant impact on longevity of seniors. Where a person lives and not just how they choose to live, can make a huge difference. This was discovered by an innovative study which examined seniors across the US and concluded that some places enhance longevity more than others.
There are certain locations in the US that seem to have a significant impact on longevity of seniors. Where a person lives and not just how they choose to live, can make a huge difference. This was discovered by an innovative study which examined seniors across the US and concluded that some places enhance longevity more than others. Standard scientific opinion has blamed weight gain on an excess of calories which is due to burning fewer than taken in. In opposition to this viewpoint, the carbohydrate-insulin model shows that the quality of diet matters more than calorie intake for weight loss. The model’s position is that eating processed carbohydrates and starchy foods leads to changes in hormone and insulin levels which results in an increase in fat deposition.
Standard scientific opinion has blamed weight gain on an excess of calories which is due to burning fewer than taken in. In opposition to this viewpoint, the carbohydrate-insulin model shows that the quality of diet matters more than calorie intake for weight loss. The model’s position is that eating processed carbohydrates and starchy foods leads to changes in hormone and insulin levels which results in an increase in fat deposition. Researchers who have previously discovered a method that turns skin cells into primitive like muscle cells that can be left in a lab indefinitely without losing their potential to turn into mature muscle, have now discovered how this method works and also what molecular changes it prompts within cells.
Researchers who have previously discovered a method that turns skin cells into primitive like muscle cells that can be left in a lab indefinitely without losing their potential to turn into mature muscle, have now discovered how this method works and also what molecular changes it prompts within cells.  Following a two year study of participants who ate a handful of walnuts every day showed lower levels of LDL(low density lipoprotein) cholesterol when compared with the participants levels at the start of the study. They also showed a reduced total cholesterol. The study was assisted from a grant by the Calfornia Walnut Commission.
Following a two year study of participants who ate a handful of walnuts every day showed lower levels of LDL(low density lipoprotein) cholesterol when compared with the participants levels at the start of the study. They also showed a reduced total cholesterol. The study was assisted from a grant by the Calfornia Walnut Commission. Recent research involving more than 30,000 heart patients has shown that becoming active in later life can be almost as beneficial to surviving as ongoing activity.
Recent research involving more than 30,000 heart patients has shown that becoming active in later life can be almost as beneficial to surviving as ongoing activity. If you are someone who makes mistakes or are forgetful when you are in a hurry, a recent study from Michigan State Univ. has discovered that meditation could help in becoming less prone to error. The team tested how meditation that focuses awareness on thoughts, feelings and sensations or open monitoring meditation, alters brain activity in such a manner that has suggested increased error recognition.
If you are someone who makes mistakes or are forgetful when you are in a hurry, a recent study from Michigan State Univ. has discovered that meditation could help in becoming less prone to error. The team tested how meditation that focuses awareness on thoughts, feelings and sensations or open monitoring meditation, alters brain activity in such a manner that has suggested increased error recognition. A new study has challenged what scientists in general believe about cognitive function including executive function, reasoning skills, and attention decline as people age. The new study has suggested that executive functioning and orienting actually improve with age.
A new study has challenged what scientists in general believe about cognitive function including executive function, reasoning skills, and attention decline as people age. The new study has suggested that executive functioning and orienting actually improve with age. Consuming a hot dog could actually cost a person 36 minutes of living a healthy life, while consuming a handful of nuts could help a person gain 26 minutes of an extra healthier life. A study looked at more than 5,800 foods and ranked them by the nutritional disease that can burden humans by their consumption and also the impact they make on our environment.
Consuming a hot dog could actually cost a person 36 minutes of living a healthy life, while consuming a handful of nuts could help a person gain 26 minutes of an extra healthier life. A study looked at more than 5,800 foods and ranked them by the nutritional disease that can burden humans by their consumption and also the impact they make on our environment.  A new study has shown that by staying very hydrated throughout your lifetime, you could be reducing your chance of developing heart failure. The study has suggested that keeping great hydration can possibly prevent or at the very least slow down changes that reside in the heart that ultimately lead to heart failure.
A new study has shown that by staying very hydrated throughout your lifetime, you could be reducing your chance of developing heart failure. The study has suggested that keeping great hydration can possibly prevent or at the very least slow down changes that reside in the heart that ultimately lead to heart failure.